
DNA Decoder
ELEMENTARY
educational / science
science game
6+ years
4 levels
6+ years
4 levels
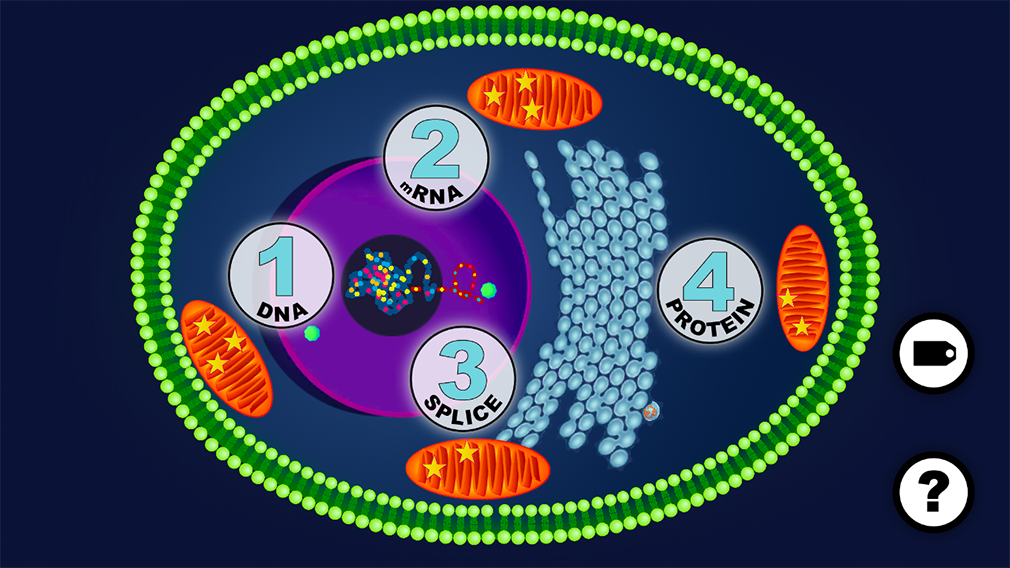
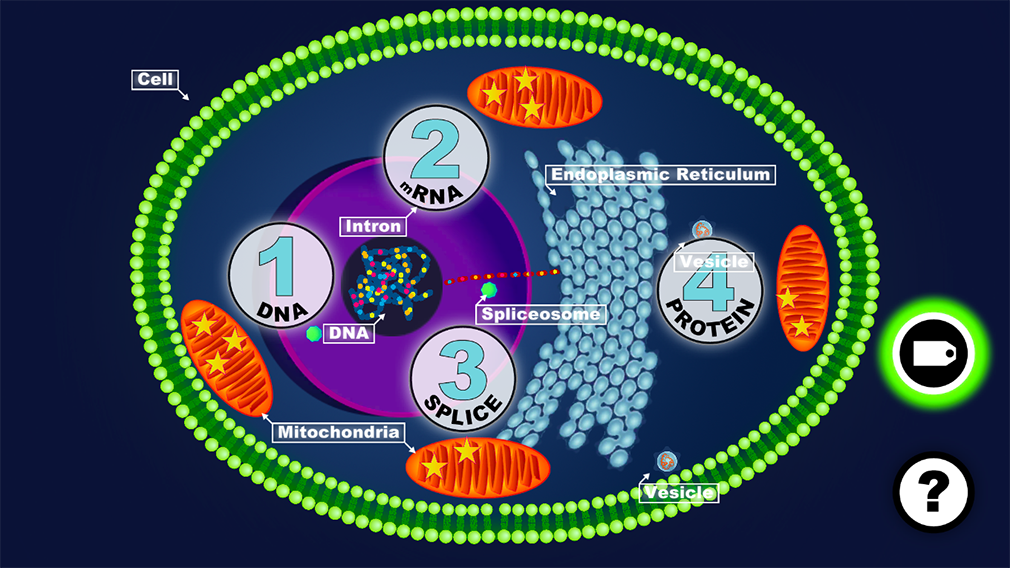
from DNA → to mRNA→ to PROTEIN
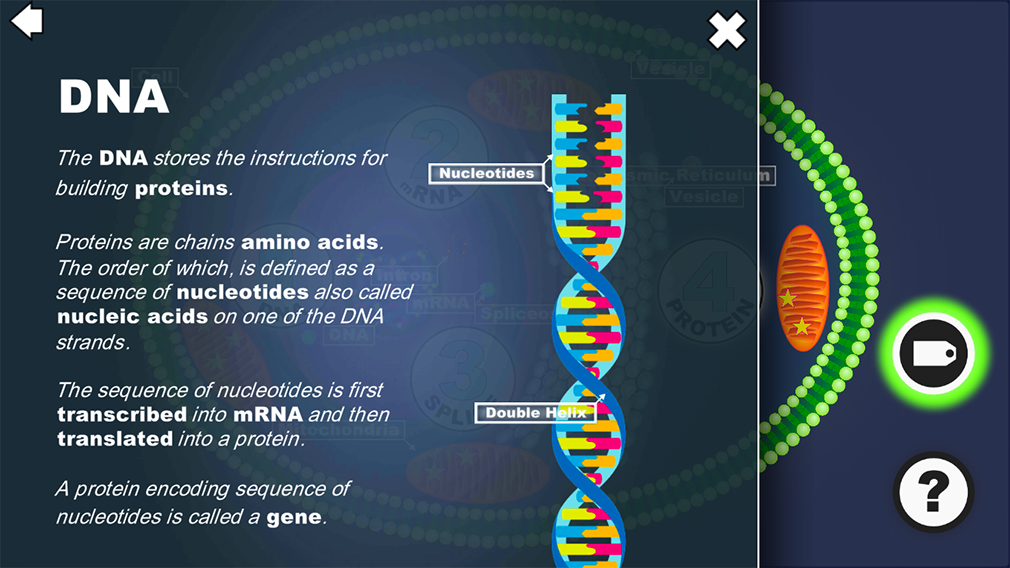
What is DNA and what is a gene?
Splice mRNA
Translate mRNA into PROTEINS
What is DNA and what is a gene?
Splice mRNA
Translate mRNA into PROTEINS
info
app for phone / tablet
kids friendly / complying with COPPA
COMPLETELY FREE
NO Ads
kids friendly / complying with COPPA
COMPLETELY FREE
NO Ads
download
SCREENSHOTS




YOU + your KID
learn about the function of DNA, RNA, PROTEINS, splicosomes and many more
Find the right GENE on the DNA
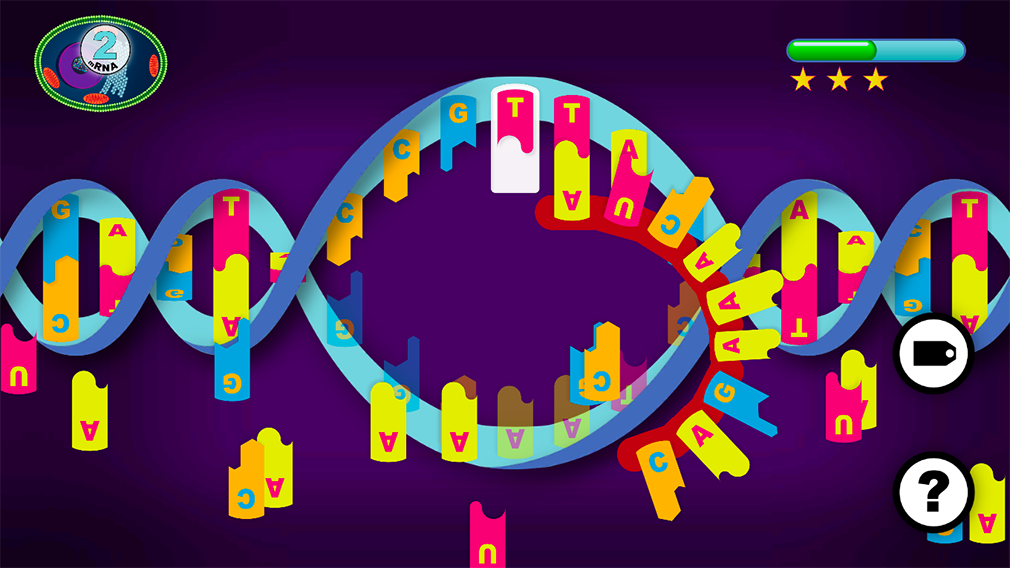
TRANSCRIBE the DNA into mRNA
SPLICE the mRNA
TRANSLATE the mRNA into PROTEIN
LEVELS

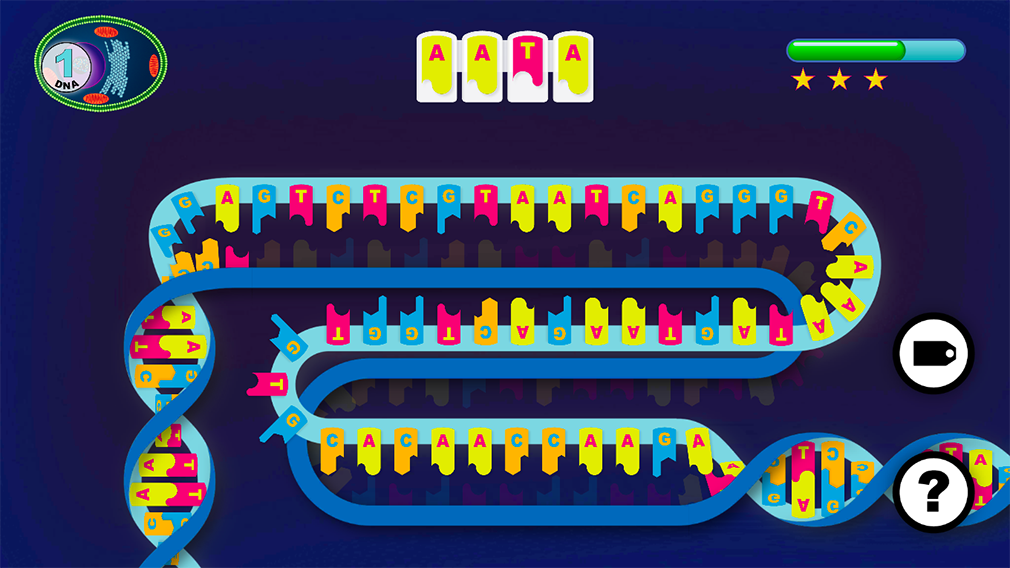
FIND
the GENE on the DNA.
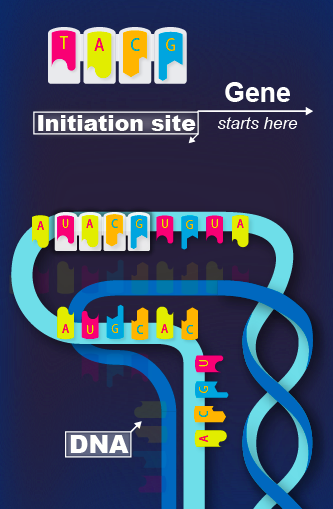
The beginning of the
GENE is marked by the
INITIATION SITE,
a special sequence of
NUCLEIC ACIDS.
GENE is marked by the
INITIATION SITE,
a special sequence of
NUCLEIC ACIDS.

GENES are segments of the DNA double helix.
DNA is a sequence of
NUCLEIC ACIDS.
DNA is a sequence of
NUCLEIC ACIDS.
GENES encodes the PROTEINS we want to create.
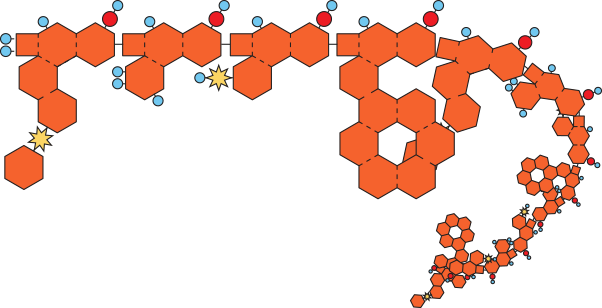
The GEOMETRY of the PROTEIN provides its FUNCTION.
→ start to create a PROTEIN
"It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material."
James Watson, Francis Crick

CREATE
mRNA – transcribe the GENE

CONNECT complementray NUCLEIC ACIDS to create a strand of messengerRNA.
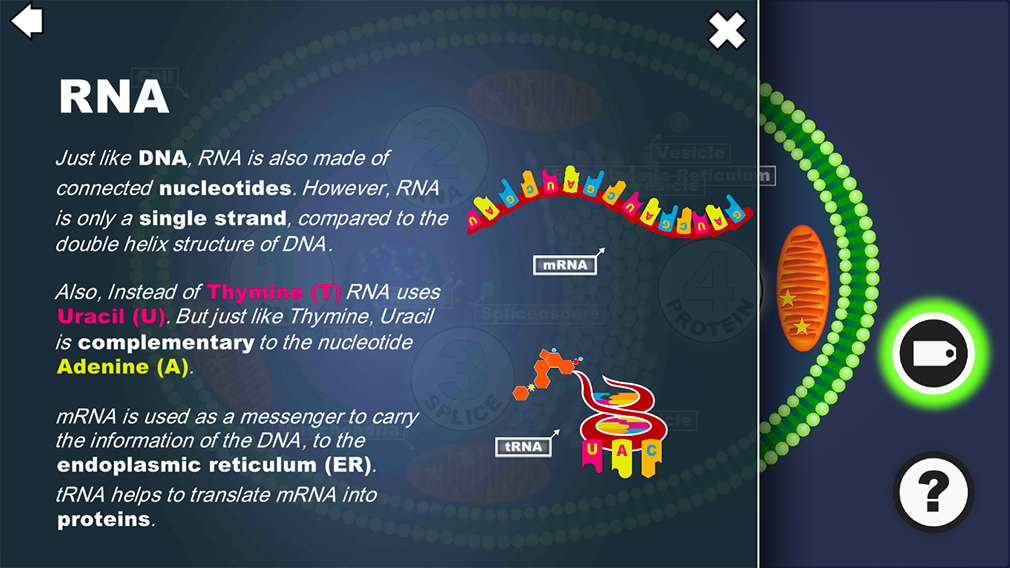
A messenger RNA is an
INVERSE COPY of the DNA.
A messenger RNA is an
INVERSE COPY of the DNA.
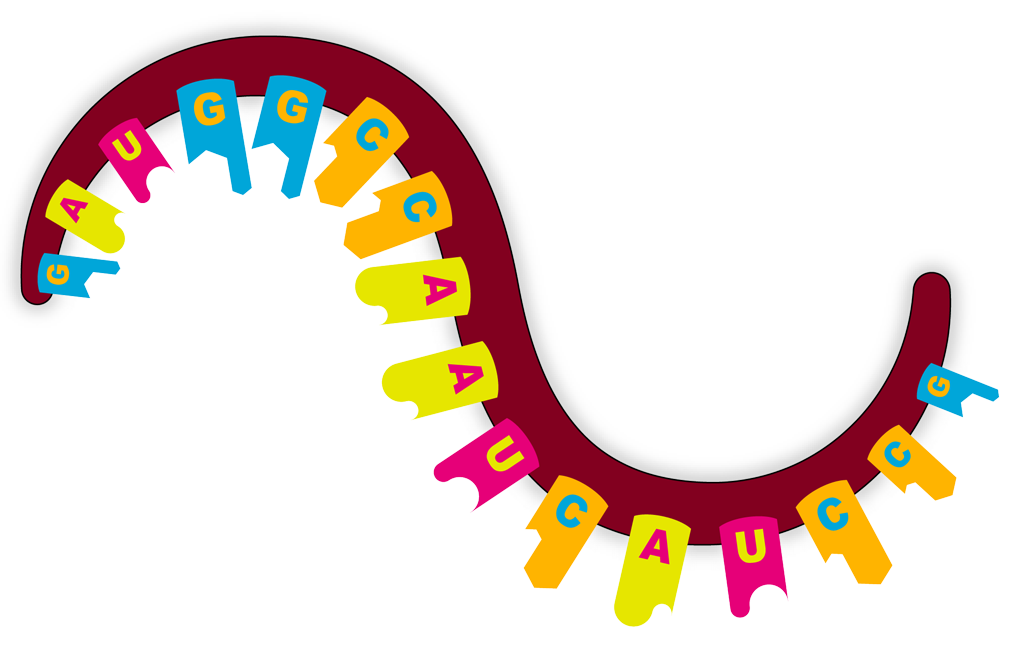
mRNA is made out of NUCLEIC ACIDS:
Adenine Guanine Cytosine Thymine / Uracil
Adenine Guanine Cytosine Thymine / Uracil

The COMBINATION provides the ENCODING of the information to create the PROTEIN.
→ start the DNA-transcription / GENE→mRNA

CUT out
non-codig sections from the mRNA
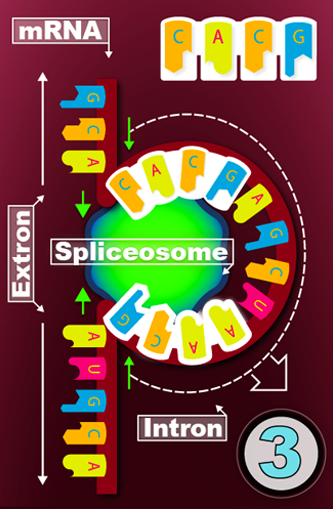
CONNECT the specific
NUCLEIC ACID sequences.
Use the SPLICEOSOME!
EXONS (coding) – are joined together
INTRONS (non-coding) – are REMOVED
NUCLEIC ACID sequences.
Use the SPLICEOSOME!
EXONS (coding) – are joined together
INTRONS (non-coding) – are REMOVED
Exons (coding) – are joined together
Introns (non-coding) – are removed
Introns (non-coding) – are removed
Whole sections will be cut out and the remaining pieces will we stiched back together.
→ remove the NON-CODING regions
The spliceosome is actually a whole bunch of proteins, that work together.

TRANSLATE
the mRNA to build a PROTEIN
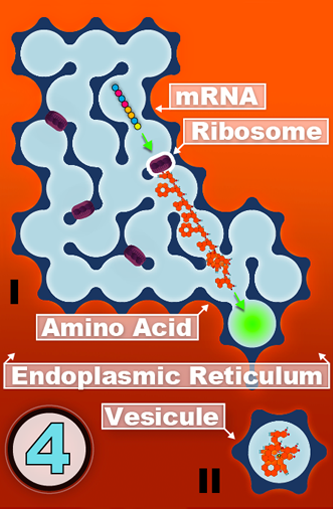
I
TAKE the mRNA to the
RIBOSOMES.
RIBOSOMES translate the mRNA
into a chain of AMINO ACIDS.
TAKE the mRNA to the
RIBOSOMES.
RIBOSOMES translate the mRNA
into a chain of AMINO ACIDS.
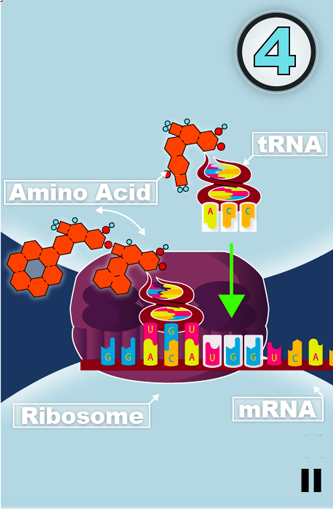
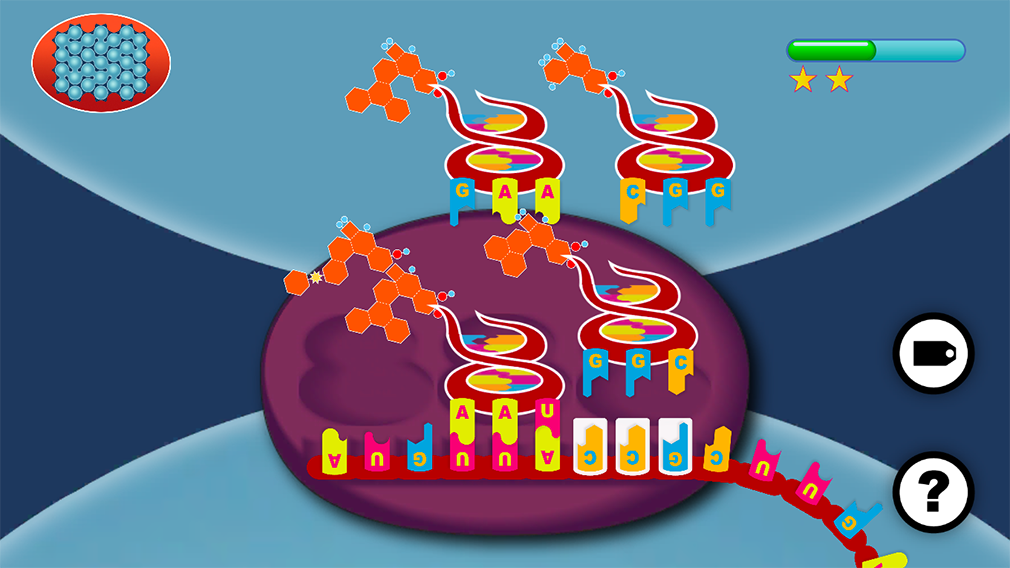
II
FIND the right transfer RNA
to fit your mRNA sequence.
1 tRNA contains a set of 3 NUCLEIC ACIDS
1 tRNA ≙ 1 AMINO ACID.
FIND the right transfer RNA
to fit your mRNA sequence.
1 tRNA contains a set of 3 NUCLEIC ACIDS
1 tRNA ≙ 1 AMINO ACID.
→ translate the mRNA to build a PROTEIN
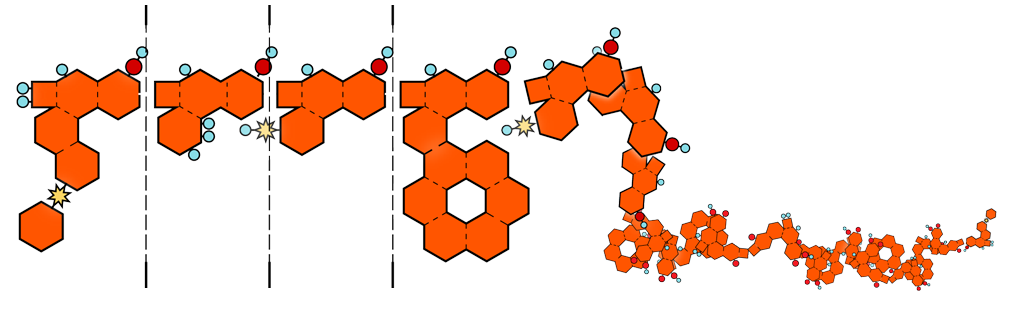
Proteins are the building blocks of life.
Almost every process in our body involves proteins.
They act as enzymes, facilitators and antibodies.
Almost every process in our body involves proteins.
They act as enzymes, facilitators and antibodies.
Proteins are produced by the ribosomes (which is in itself an assembly of many proteins).
Since proteins are made up of 20 different amino acids, three nucleic bases are needed to encode them all. These three bases are called the codon.
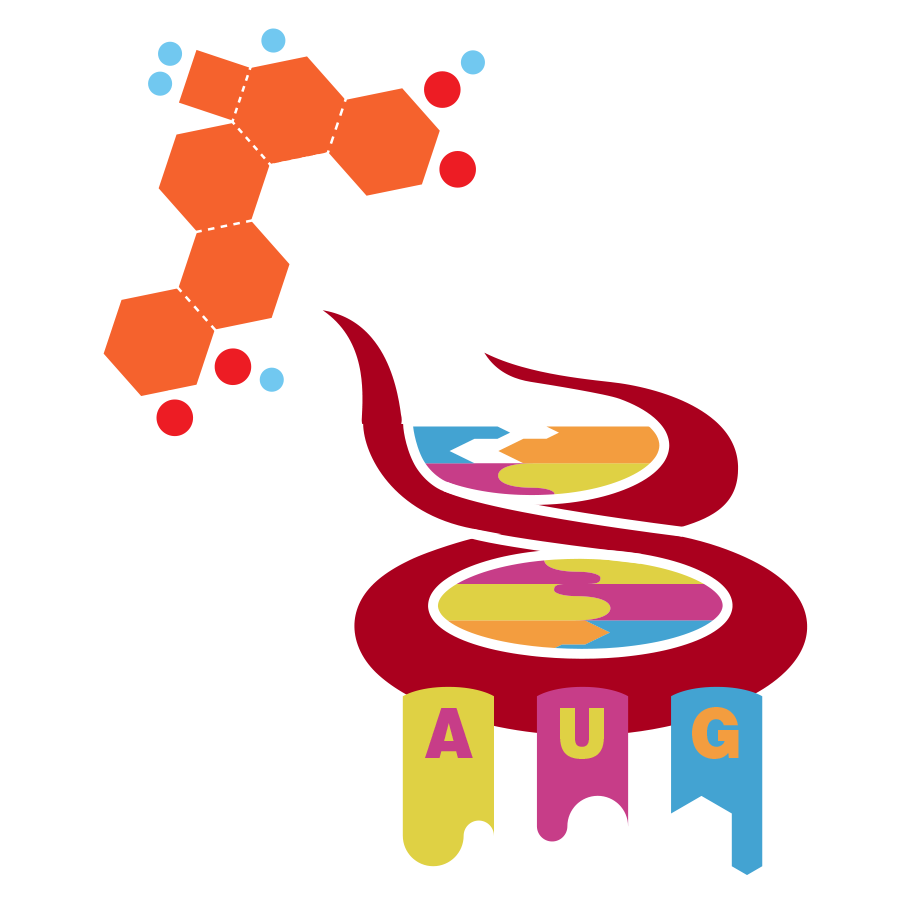
The mRNA is pulled through the ribosome. The ribosome then attaches a special kind of molecule called transfer RNA or tRNA to the mRNA. Each tRNA exposes a three bases long anti-codon.
Each tRNA also carries with it an amino acid, which matches the anti-codon.
Each tRNA also carries with it an amino acid, which matches the anti-codon.
The ribosome then takes each amino acid, and attaches them one after the other, while the mRNA is pulled through.
This is how the mRNA gets translated into a protein. Always three bases at a time.
DNA is located inside the nucleus, while the production of proteins is located outside the nucleus.
DNA is located inside the nucleus, while the production of proteins is located outside the nucleus.
my kid is an alien
download


 my Kid is an Alien
my Kid is an Alien